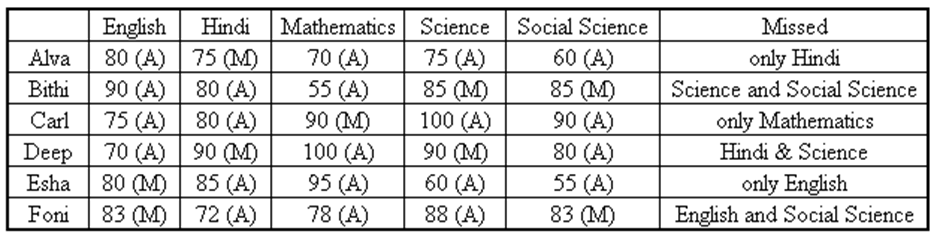
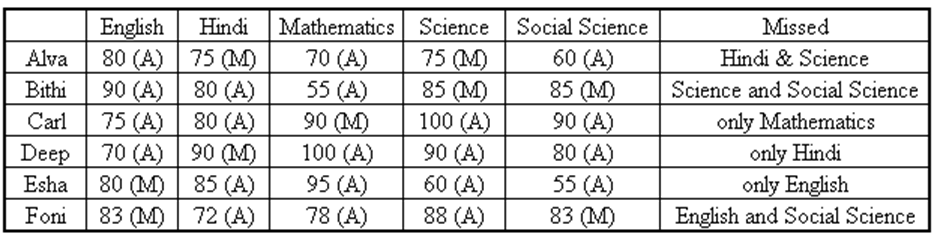
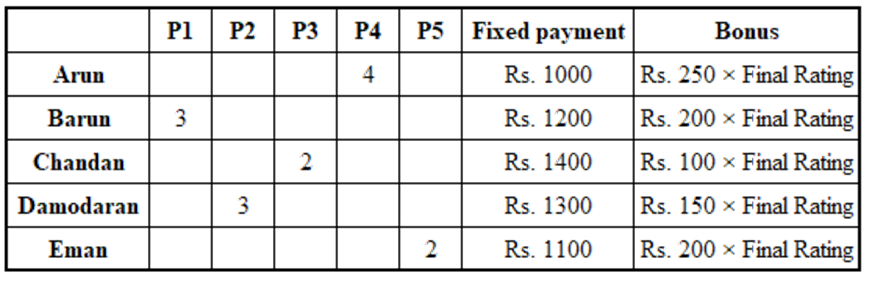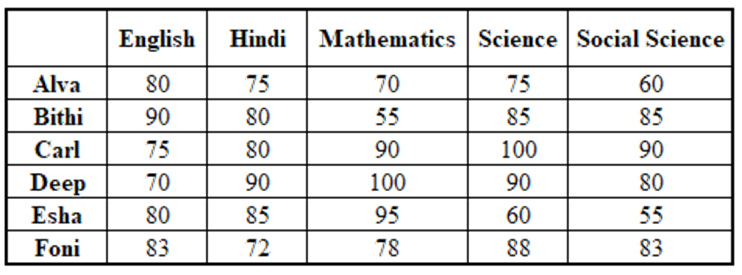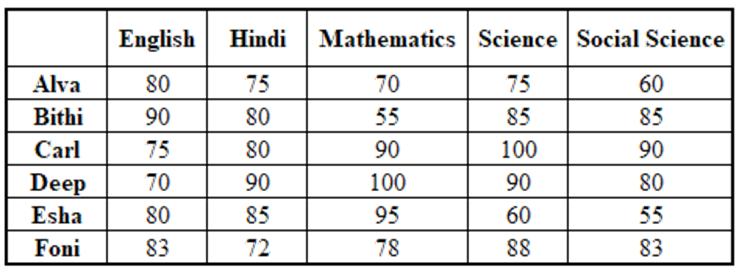Directions for questions 47 to 50:
Answer the following questions based on the information given below.
Questions 47 to 50 carry 3 marks each.
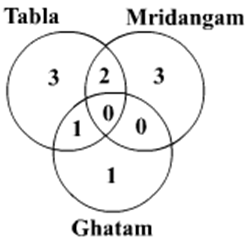
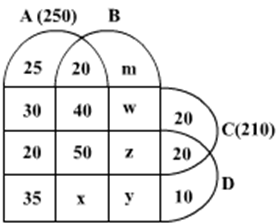
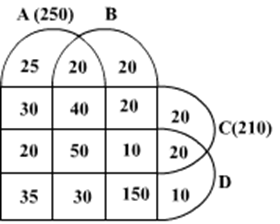
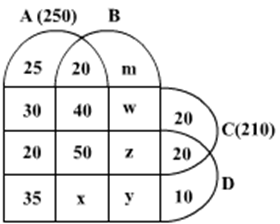
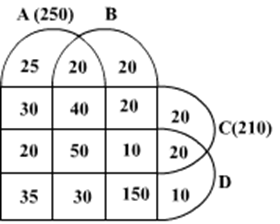
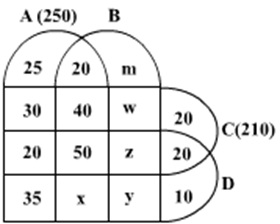
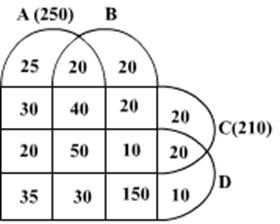
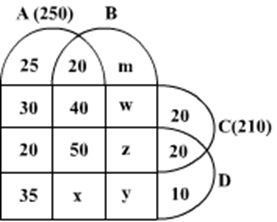
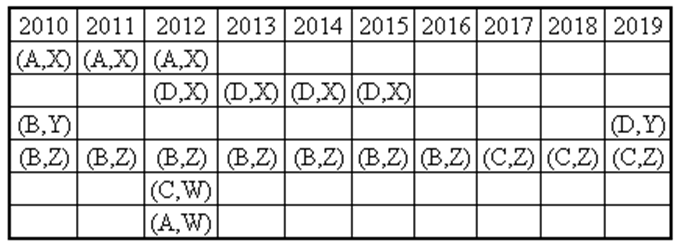
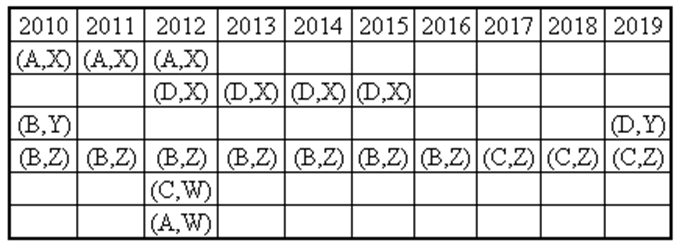
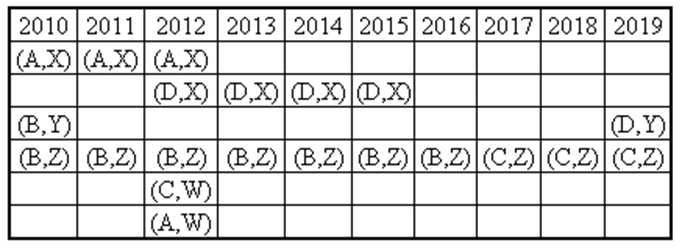
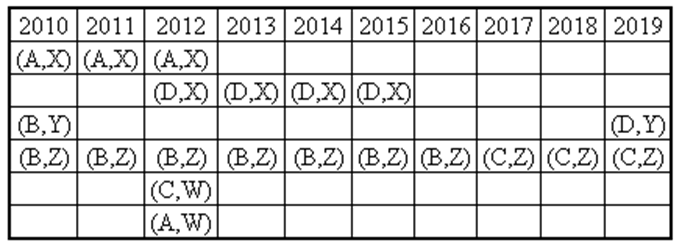
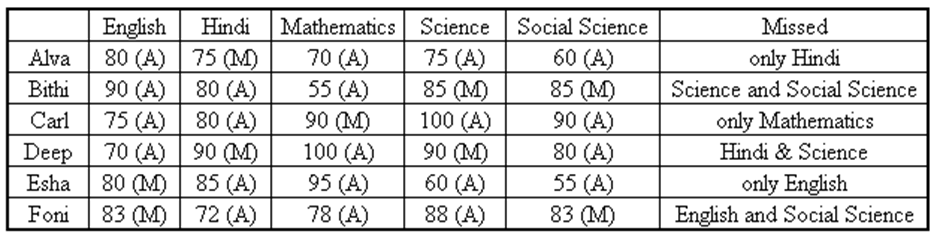
Ten musicians (A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I and J) are experts in at least one of the following three percussion instruments: tabla, mridangam, and ghatam. Among them, three are experts in tabla but not in mridangam or ghatam, another three are experts in mridangam but not in table or ghatam, and one is an expert in ghatam but not in tabla or mridangam. Further, two are experts in tabla and mridangam but not in ghatam, and one is an expert in tabla and ghatam but not in mridangam.
The following facts are known about these ten musicians.
- Both A and B are experts in mridangam, but only one of them is also an expert in tabla.
- D is an expert in both tabla and ghatam.
- Both F and G are experts in tabla, but only one of them is also an expert in mridangam.
- Neither I nor J is an expert in tabla.
- Neither H nor I is an expert in mridangam, but only one of them is an expert in ghatam.
Q. 1.
If C is an expert in mridangam and F is not, then which are the three musicians who are experts in tabla but not in either mridangam or ghatam?
- A).
C, E and G
- B).
E, G and H
- C).
C, G and H
- D).
E, F and H